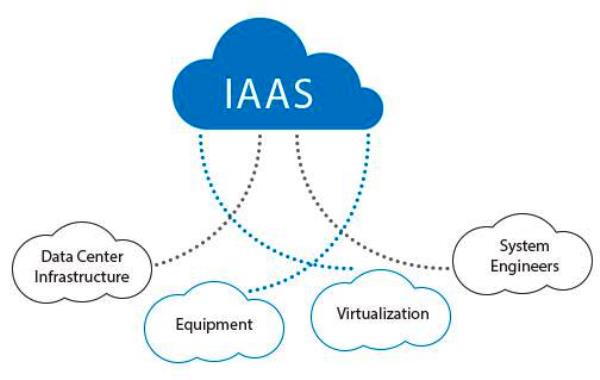
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is changing how businesses manage their IT needs.
It offers virtualized resources over the internet, allowing companies to rent servers, storage, and networking without the hassle of managing physical hardware.
What is IaaS?
IaaS is a cloud model that lets businesses rent computing resources on a pay-as-you-go basis.
This approach is flexible and scalable, enabling companies to adjust their infrastructure as needed.
Benefits of IaaS
Scalability and Flexibility:
IaaS allows businesses to scale their infrastructure up or down depending on demand, helping them stay agile and efficient.
Cost-Efficiency:
With IaaS, businesses avoid upfront costs for hardware. They only pay for what they use, making IT spending more predictable.
Fast Deployment:
IaaS makes it quick and easy to set up resources, allowing businesses to launch new projects faster.
Focus on Core Goals:
By letting IaaS providers handle infrastructure, businesses can focus on improving their products and services.
Global Reach:
IaaS providers have data centers worldwide, so businesses can reach users globally and improve app performance.
Reliability:
IaaS ensures high availability and redundancy, reducing downtime and improving user experience.
Challenges
Security:
Even though IaaS providers have strong security, businesses must take steps to protect their data and ensure compliance.
Vendor Lock-in:
It’s important to be aware of potential vendor lock-in. Businesses should plan for data portability and consider future flexibility when choosing a provider.
Read more about Virtualization in Computing…
Conclusion
IaaS offers businesses a flexible, cost-effective way to manage IT infrastructure.
It enables them to scale quickly, save on costs, and focus on innovation while ensuring reliable and secure services.